SHARM EL-SHEIKH, November 10, 2022 — WTW (NASDAQ: WTW) today unveiled ground-breaking technology designed to increase the resilience of the world’s agriculture and food supply, which is becoming increasingly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, with more frequent and extreme weather events. This announcement comes two days before the COP27 Adaptation and Agriculture Day on Saturday 12 November, when nations will come together to address how to make food systems more resilient.
Developed by the Climate and Resilience Hub at WTW, Climate Quantified™ CROP is able to project the individual climate risks most likely to impact each of the world’s agricultural crops (including staple and niche crops). Key capabilities of the new technology include:
According to a recent UN report, climate change is rated as the biggest threat to food security, with up to 828 million people in the world affected by hunger in 20211. In addition, an estimated 2.3 billion people faced moderate or severe food insecurity, bringing the number of people unable to access a healthy diet to 3.1 billion, or about 40% of humanity.
John Firth, Senior Director, Climate and Resilience Hub at WTW, said: “The resilience of our global food system has taken a battering from successive droughts and ongoing supply chain shocks, putting food supplies at risk for millions. It is crucial to identify the vulnerable links of the agricultural supply chain induced by climate change and then strengthen them”.
“Climate Quantified™ CROP is an innovative approach to rapidly identify regions in the world that will experience the most profound changes in extreme weather events and so where the greatest risks are across the global production of individual crops. The technology also offers the unique capability of being able to guide decisions on the most suitable areas to grow specific crops, helping to inform critical, longer-term decisions for supply chains.”
Climate Quantified™ CROP will have the capacity to analyse more than 40 different crops when it goes live in 2023. Compared to systems available in the market, the WTW technology has the unique capability of identifying the projected changes in growth suitability for a particular crop, highlighting the changes in causes - such as heat stress, extreme rainfall, flooding (fluvial and coastal), drought, storms and wildfire – that are driving area-specific changes in yield and production.
Using the most up-to-date climate model simulations from the latest high resolution Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) data2, Climate Quantified™ CROP analyses climate hazards specifically tailored to the unique climate sensitivities and thresholds of each individual crop. The tool is then able to clearly identify the level of suitability from one of four categories - highly suitable, moderately suitable, marginally suitable and unsuitable – for a particular crop to grow for present-day and multiple future scenarios.
A recent study by NASA shows that global production of maize is projected to decline by 24% within 10 years due to climate change, while wheat could potentially see growth of about 17% during the same period3. These changes are due to projected increases in temperature, shifts in rainfall patterns and elevated surface carbon dioxide concentrations from human-caused greenhouse gas emissions.
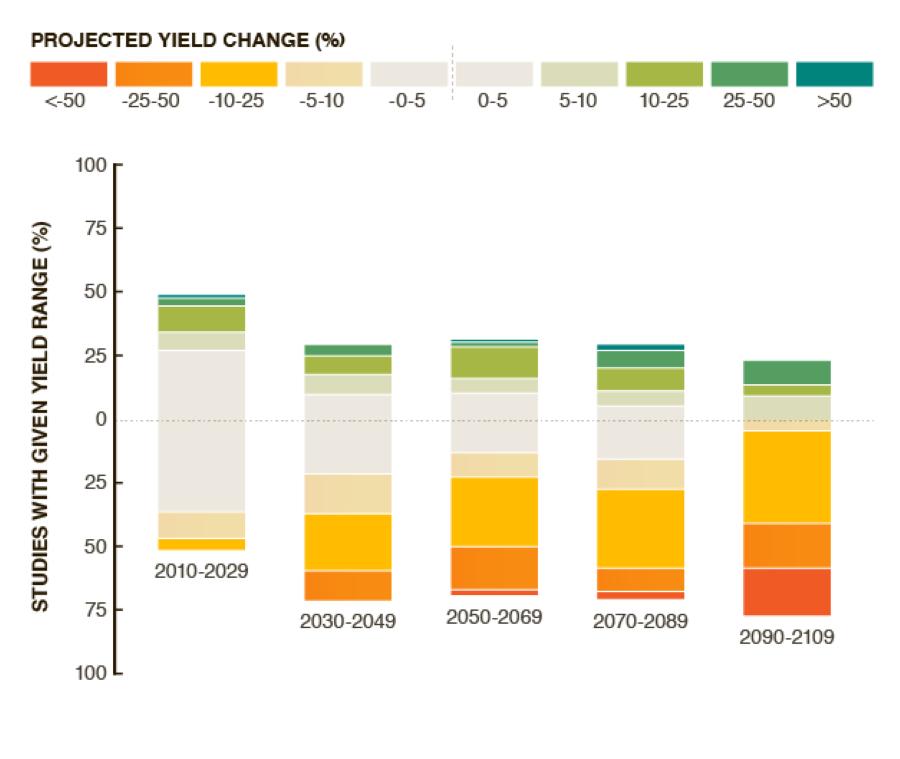
(Source: Challinor AJ, Watson J, Lobell DB, Howden SM, Smith DR, Chhetri N. 2014. A meta-analysis of crop yield under climate change and adaptation. Nature Climate Change 4: 287 – 291).
In order to adapt to these sudden changes in crop yields, Climate Quantified™ CROP can be used by farmers to guide implementation of appropriate resilience-building measures and mitigate risk to crops and livelihoods. At corporate level, food and beverages companies for example can use the technology to inform sourcing decisions for critical commodities and mitigate supply chain risks. The technology can also be used by financial institutions to support long-term investment decisions and by humanitarian organisations to better understand and prepare for future food security challenges.
Firth said “The world is clearly not on target to stabilise the climate at 1.5°C or 2°C, reinforcing the need for agricultural supply chains to face the reality of the devastating climatic effects on the world’s food supply. It is also not enough to simply understand the future risks. While the first step is to identify the risks, it is crucial that we implement actions to manage these risks. Talking and planning is not enough – we have to act now. That is a vital component of building a resilient supply chain.
“Climate Quantified™ CROP is a practical and innovative solution to the real-world challenge of strengthening global food security”
John Firth | Senior Director, Climate and Resilience Hub at WTW
“Climate Quantified™ CROP is a practical and innovative solution to the real-world challenge of strengthening global food security over the coming decades in the face of severe climatic instability.”
Erin Owain, Alvaro Linares Fuster, Flavia Olivieri, Cameron Brown
Uriel Zajaczkovski, Carl Giardina, Ayomide Akintoye
At WTW (NASDAQ: WTW), we provide data-driven, insight-led solutions in the areas of people, risk and capital. Leveraging the global view and local expertise of our colleagues serving 140 countries and markets, we help organisations sharpen their strategy, enhance organisational resilience, motivate their workforce and maximise performance.
Working shoulder to shoulder with our clients, we uncover opportunities for sustainable success—and provide perspective that moves you.
The Climate and Resilience Hub (CRH) is the focal point for our climate expertise and capabilities, pooling knowledge from across our people, risk and capital businesses and from our collaborations to deliver climate and resilience solutions in response to a range of regulatory, investor, consumer, employee and operating pressures. Under the Climate Quantified™ brand we deliver analytics, advice and transactions to enable corporate, finance and public sector institutions to embrace the climate decade ahead.
1 UN Report: Global hunger numbers rose to as many as 828 million in 2021, 6 July 2022.
2 CMIP was established in 1995 by the World Climate Research Programme to better understand the past, present and future of the climate system. Now in its sixth phase, the state-of-the-art CMIP6 projections cover the entire globe and the datasets it has produced have underpinned the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Assessment Reports.
3 Jägermeyr et al. 2021